Car Polymer (Plastic)
Oxidation AND RESTORATION
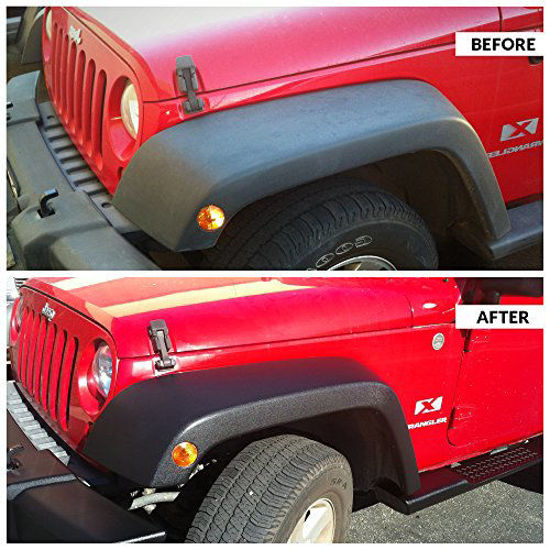
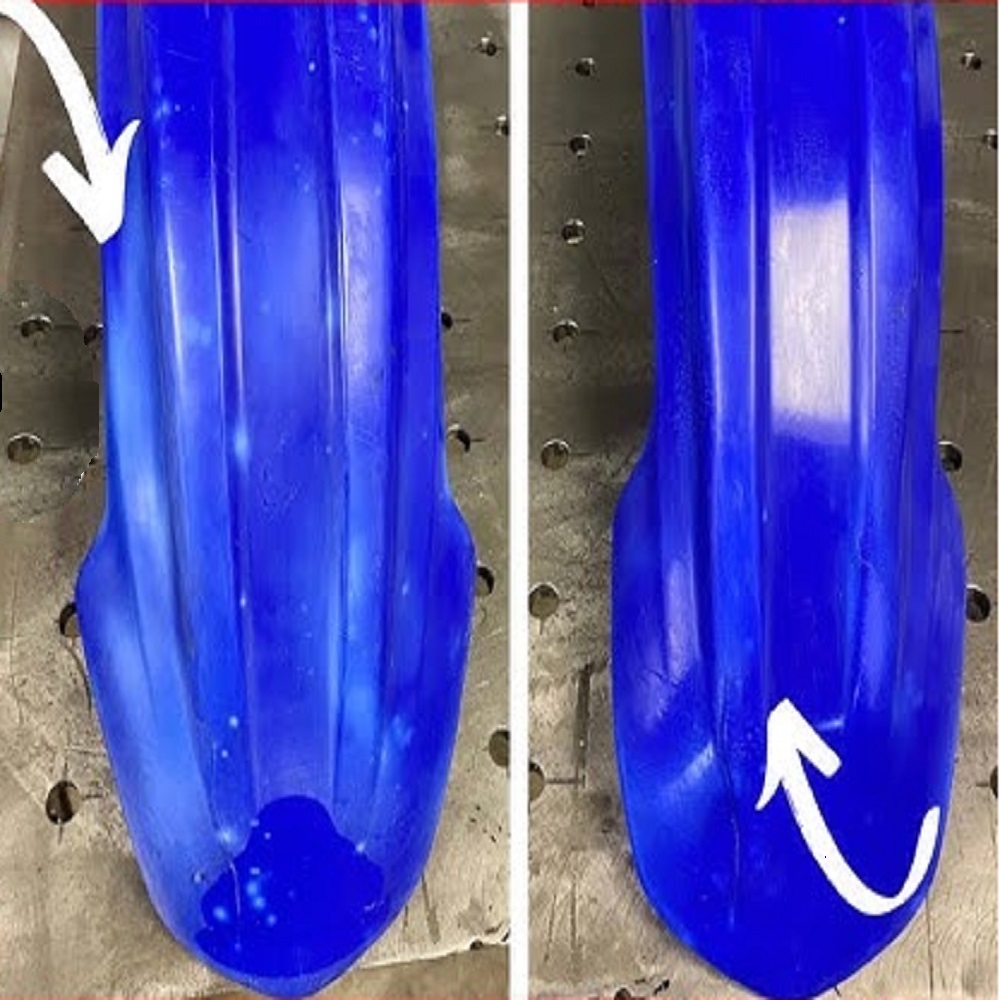
Car Plastic trim degradation and restoration using Proactor Antioxide Solution
Car plastic trim (polymer) degradation involves a change in the properties of polymers as they are exposed to natural elements during their service life. Polymers can degrade through various mechanisms, including thermal degradation, photo-oxidation, hydrolysis, biodegradation, and chemical degradation. Factors such as temperature, oxygen exposure, UV radiation, and polymer structure influence the rate and extent of degradation. The changes are often gradual and negatively impact the stability of polymers, resulting in the deterioration of surface, physical and mechanical properties over time. In automotive applications, polymer degradation can lead to increased risk of excessive VOC emissions, fogging, odor, color fading, and surface crazing, among other issues.
Black plastic trims always fade to an ugly grey over time and daily wear and tear. Your plastic and rubber trims brave harmful UV rays, dust and other contaminants on a daily basis which results in discoloration and an old grey look.
Our Proactor Antioxidant is a trim restoration solution and not only protects against future damage, but also brings back the original black shine on all your plastic trims, rubber trims, bumpers, window seals and cladding.
Use on Trim and Bumpers: oxidised or faded paint is not the only DIY application for Proactor Antioxide solution. Exterior trim and bumpers that have surface oxidation caused by prolonged exposure to the sun and other elements, can be reconditioned by simply wiping the serum over the selected areas with a cotton cloth. Apply thinly and see instant results.
Use on Scratches and Swirls: Minor scratches like those around doors, and swirl marks on trunks and hoods where packages have been placed and moved, become immediately invisible after wiping with Proactor Antioxide solution. This quick and easy Do-It-Yourself procedure will bring back the original appearance by eliminating unsightly blemishes.

The videos on this web site will show you how to repair or restore your car exterior plastic trim against oxidation and bring back the shine to exterior trim and plastics, in a simple Do-It-Yourself (DIY) operation. Simply hand wash the panels to be treated and allow to dry, then wipe on a thin layer of Proactor Antioxide solution.
Guarantee: We offer a money back guarantee if the product is not as specified or if dissatisfied for any reason. For further information, go to the Shipping Page – Return Policy
How to Use
Preparation – This is the most important step.
- All loose dirt and old polish and waxes must be removed to allow the serum to contact the oxidised areas. Failure to do this may result in a streaky looking finish.
- A preferred cleaning method uses a normal hand
wash (not a commercial car wash) using liquid dish
washing soap and a sponge. Hard rubbing is NOT
required.
- Wet and Dry sandpaper can be used to smooth any clear coat ridges. We recommend 1000 grit or finer but be careful not to sand through to the underlying metal.
- Thoroughly rinse off the surfaces to remove all soap suds and allow the car to dry.
Application
- When the car is completely dry, wipe on a thin layer of serum, using an open weave cotton cloth, to all affected panels (usually the hood, roof and trunk). A piece of an old white cotton tank top, undershirt or T-Shirt is very suitable.
- A thick layer of serum will NOT improve results and may form ridges that are very hard to remove. A single bottle of serum is enough to treat a full sized car – twice.
- Best results are obtained at temperatures above 50° F. (10° C) but panel surfaces should NOT be hot.
- A dust free environment is NOT required.

After Care
- After several hours, press a fingertip lightly onto the surface. If the fingerprint remains, allow a longer time for the initial set.
- After a light fingerprint is no longer visible, vehicle may be driven while the serum continues to set, but do not expose to moisture (rain, sprinklers, fog, frost or snow) for 24 hours, as this will likely cause a streaky finish and/or water spots.
- When fully set (allow 3 to 5 days at least) a second coat should be applied for a better and longer lasting finish.
- Before applying the second coat, wash off any dirt with plain water and a sponge. Allow to dry.
Polish
It is not necessary to apply polish over the set serum, but a polish such as Carnauba wax can be applied. However, a second coat of serum is easier to apply and will provide a comparable finish.
The Finished Results
The oxidation on the cars in the above photos was so severe, that repainting seemed to be the only alternative. By following the recommended steps outlined above, the improvement in the appearance of the vehicles was outstanding and achieved with minimal effort, no special tools and at minimum cost.
Causes
of Polymer Degradation in Automotive Applications
The automotive industry relies on the use of polymers for a range of applications and components. These polymers must withstand the harsh conditions to which they are exposed during service to maintain their physical and surface properties. Several factors contribute to polymer degradation in automotive applications, and it is imperative for OEMs to consider related risks when designing and processing polymers. Choosing the right polymer additives for a specific application is essential to avoid polymer degradation and deliver optimal performance. High-performance UV stabilizers and antioxidants deliver superior protection to polymers against degradation to improve the durability of automotive components for interior and exterior applications.
What is Polymer Degradation?
Polymer degradation involves a change in the properties of polymers as they are exposed to natural elements during their service life. The changes are often gradual and negatively impact the stability of polymers, resulting in the deterioration of surface, physical and mechanical properties over time. In automotive applications, polymer degradation can lead to increased risk of excessive VOC emissions, fogging, odor, color fading, and surface crazing, among other issues.
Weathering of Polymers
Weathering also plays a role in the degradation of thermoplastic polyolefins (TPO) automotive parts. Exterior car parts, such as bumpers and door trim, are routinely exposed to natural elements, continuously enduring exposure to UV light and extreme temperatures. Polymers for automotive interior applications, including instrument panels, dashboards and seat back covers, are also vulnerable to UV light and extreme temperatures. After long-term exposure to these elements, components can discolor and begin to deteriorate. Early signs of weathering degradation include fading and discoloration.
Exposure of Polymers to Pollution
Air pollution can also serve as a catalyst for degradation in polymer-based automotive parts. Pollutants from car exhaust, as well as general air pollution, accelerate polymer degradation, especially in exterior applications, such as bumpers and door trim. Chemical degradation compromises the integrity of the polymer chains that make up the component, which significantly decreases performance capabilities and longevity, and may also jeopardize overall vehicle safety.
Increasing the Life Span of Plastics with Antioxidants
One of the greatest benefits to using plastics is their longevity. However, when certain polymers are placed in adverse conditions, like extreme heat or exposure to certain chemicals, they can break down faster. For the plastics used in automotive injection molding and thermoforming, we use plastics with antioxidants added in to increase its lifespan and durability. But how do antioxidants work for plastic? Are they the same as the antioxidants in vitamins? Our injection molding company is going to answer these questions and more.
How Do Antioxidants in Plastics Work?
This is where antioxidants come in. Antioxidants neutralize the free radical molecules that speed up oxidation and lead to damage. You have probably heard of antioxidants for your health - vitamin C, beta carotene, and lycopene are examples of powerful antioxidants found in food that we can eat to slowdown free radicals from attacking our cells. If you dip a sliced apple in lemon juice, it won't turn brown as quickly because the vitamin C slows down the oxidation process my neutralizing free radicals.
Types of Antioxidants
There are two main types of antioxidants used in plastic:
Primary Antioxidants: They
are radical scavengers that remove alkyl radials
that occur when high temperatures snap the polymer
chains and hydroxyl radicals that develop from
abstract hydrogen; Examples include hindered
phenols;
Secondary antioxidants: These
remove organic hydroperoxides that are formed when
primary antioxidants remove free radicals. If not
removed, hydroperoxides can cause fresh radical
reactions. Examples include phosphites and
thioethers;
Typically, blends of both primary and secondary antioxidants work together for a superior process. In injection molding, phosphites stabilize the plastic during the melting process while thioethers are ideal for plastics that are frequently exposed to heat during its usage. Antiozonants also prevent and slow degradation of polymers caused by ozone. This is more likely to affect rubber where ozone can lead to cracking, but it can also affect plastics.
Always Free Shipping

How to Restore oxidised and Faded Car Paint